Description
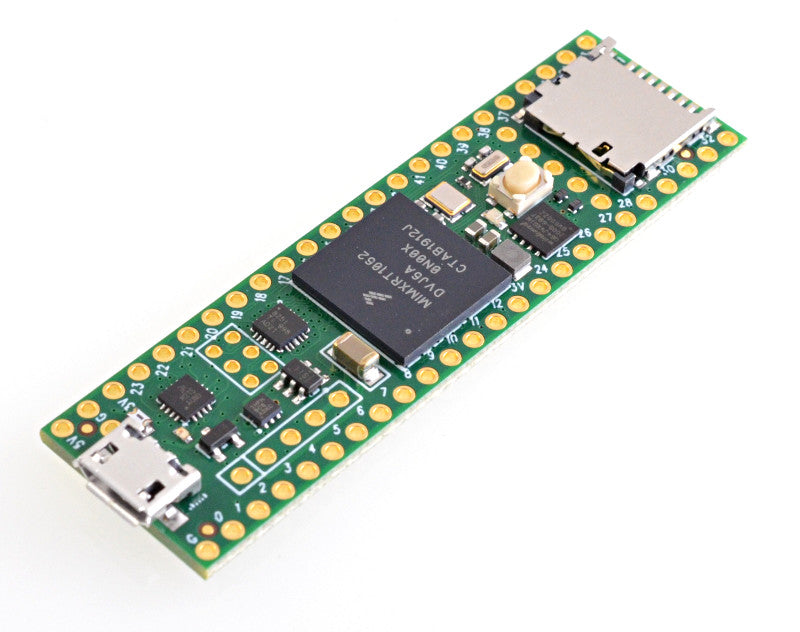
The Teensy 4.1 is newest iteration of the astoundingly popular development platform that features an ARM Cortex-M7 processor at 600MHz, with a NXP iMXRT1062 chip, four times larger flash memory than the 4.0, and two new locations to optionally add more memory. The Teensy 4.1 is the same size and shape as the Teensy 3.6 (2.4in by 0.7in), and provides greater I/O capability, including an ethernet PHY, SD card socket, and USB host port.
When running at 600 MHz, the Teensy 4.1 consumes approximately 100mA current and provides support for dynamic clock scaling. Unlike traditional microcontrollers, where changing the clock speed causes wrong baud rates and other issues, Teensy 4.1 hardware and Teensyduino's software support for Arduino timing functions are designed to allow dynamically speed changes. Serial baud rates, audio streaming sample rates, and Arduino functions like delay() and millis(), and Teensyduino's extensions like IntervalTimer and elapsedMillis, continue to work properly while the CPU changes speed. Teensy 4.1 also provides a power shut off feature. By connecting a pushbutton to the On/Off pin, the 3.3V power supply can be completely disabled by holding the button for five seconds, and turned back on by a brief button press. If a coin cell is connected to VBAT, Teensy 4.1's RTC also continues to keep track of date & time while the power is off. Teensy 4.1 also can also be overclocked, well beyond 600MHz!
Note: Please be aware that the Teensy 4.1 does not include headers and will need to be purchased separately and soldered on yourself.
The ARM Cortex-M7 brings many powerful CPU features to a true real-time microcontroller platform. The Cortex-M7 is a dual-issue superscaler processor, meaning the M7 can execute two instructions per clock cycle, at 600MHz! Of course, executing two simultaneously depends upon the compiler ordering instructions and registers. Initial benchmarks have shown C++ code compiled by Arduino tends to achieve two instructions about 40% to 50% of the time while performing numerically intensive work using integers and pointers. The Cortex-M7 is the first ARM microcontroller to use branch prediction. On M4, loops and other code which much branch take three clock cycles. With M7, after a loop has executed a few times, the branch prediction removes that overhead, allowing the branch instruction to run in only a single clock cycle.
Tightly Coupled Memory is a special feature which allows Cortex-M7 fast single cycle access to memory using a pair of 64 bit wide buses. The ITCM bus provides a 64 bit path to fetch instructions. The DTCM bus is actually a pair of 32 bit paths, allowing M7 to perform up to two separate memory accesses in the same cycle. These extremely high speed buses are separate from M7's main AXI bus, which accesses other memory and peripherals. 512 of memory can be accessed as tightly coupled memory. Teensyduino automatically allocates your Arduino sketch code into ITCM and all non-malloc memory use to the fast DTCM, unless you add extra keywords to override the optimized default. Memory not accessed on the tightly coupled buses is optimized for DMA access by peripherals. Because the bulk of M7's memory access is done on the two tightly coupled buses, powerful DMA-based peripherals have excellent access to the non-TCM memory for highly efficient I/O.
Teensy 4.1's Cortex-M7 processor includes a floating point unit (FPU) which supports both 64 bit "double" and 32 bit "float". With M4's FPU on Teensy 3.5 & 3.6, and also Atmel SAMD51 chips, only 32 bit float is hardware accelerated. Any use of double, double functions like log(), sin(), cos() means slow software implemented math. Teensy 4.1 executes all of these with FPU hardware.
- ARM Cortex-M7 at 600MHz
- 1024K RAM (512K is tightly coupled)
- 128Mb Flash (64K reserved for recovery & EEPROM emulation)
- USB Host Port
- 2 Additional Flash Memory Locations
- 3 CAN Bus (1 with CAN FD)
- 2 I2S Digital Audio
- 1 S/PDIF Digital Audio
- 1 SDIO (4 bit) native SD
- 3 SPI, all with 16 word FIFO
- 3 I2C, all with 4 byte FIFO
- 7 Serial, all with 4 byte FIFO
- 32 general purpose DMA channels
- 31 PWM pins
- 40 digital pins, all interrrupt capable
- 14 analog pins, 2 ADCs on chip
- Cryptographic Acceleration
- Random Number Generator
- RTC for date/time
- Programmable FlexIO
- Pixel Processing Pipeline
- Peripheral cross triggering
- Ethernet PHY
- microSD Card Socket
- Power On/Off management